Pediatric Dentistry Services (Pedodontics)
Pediatric dentistry or Pedodontics is the branch of dentistry that addresses the treatment of dental diseases in children. The child patient is a “special” patient who needs special attention. Within the dental clinic Cluj – Ortho Implant Center – we have pedodontists specialized in treatments for children.

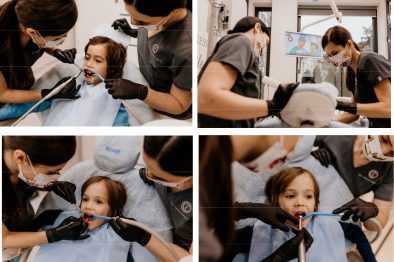
The child’s first visit to the dentist (pedodont)
The child’s first visit to the dentist is an accommodation in which the little patient meets the pedodontist. He is shown the dental chair, the instruments, and the model explains the correct brushing technique, all in the form of a play to gain the child’s confidence and make him feel as relaxed as possible. In order to have a good cooperation from the children, the visits to the pedodont must be scheduled in such a way that they do not coincide with the children’s sleep or meal schedule, and their duration must take into account the children’s age. During the treatment sessions, the children can follow their favorite drawings on the monitor attached to the dental unit (chair).
The order of the eruption of the teeth
In the case of temporary dentition , it is considered normal for the first teeth to appear around the age of 6-12 months, these teeth being the lower central incisors . After about 4-6 months the upper incisors (central + lateral) erupt, followed by the 2 lower lateral incisors . After the complete eruption of both the upper and lower incisors, the first molars of milk appear. There is a space between them and the incisor group because canines will later erupt there. Theoretically, the second molar of milk is the last temporary tooth to erupt on the arch, but lately a reversal of eruption periods can be seen between it and the canine. At the end of the eruption cycle of temporary teeth, children have 20 teeth in their mouth.
In the case of permanent dentition , the first permanent tooth to appear in the oral cavity is the 6-year-old molar , which will not replace any baby teeth, erupting behind the tooth. -the second temporary molar. Simultaneously with its appearance, the lower central incisors will change, even if, sometimes, they can precede the appearance of the first definitive molar. This is followed by the appearance of the upper incisor group (central + lateral incisors), followed by the eruption of the 2 lower lateral incisors , then the change of temporary molars with premolars . Between the eruption of the two premolars or before them, the eruption of the lower canines takes place. Upper canines erupt around the age of 12 after the eruption of upper premolars . The second permanent molar or 12-year-old molar is another permanent tooth that will not replace any baby teeth. It will erupt around the age of 12 behind the first permanent molar. After this molar appears, there are 28 teeth in the mouth. The final dentition will be completed by the appearance of the 4 molars of the mind after the age of 18.
This is the eruption order described in the books, but it is only indicative. A deviation of plus / minus 6 months is accepted as normal. Parents should not take the landmarks presented in theory ad-litteram and worry about small deviations. Starting from the same idea, it is not to worry if a child does not erupt his teeth in the order described in the book, each individual being different in this regard. As long as all the permanent teeth of a child will erupt by the age of 12-14, except for the wisdom tooth, it does not matter the order and the moment when the baby teeth fall out and the final ones erupt.
Diseases of baby teeth
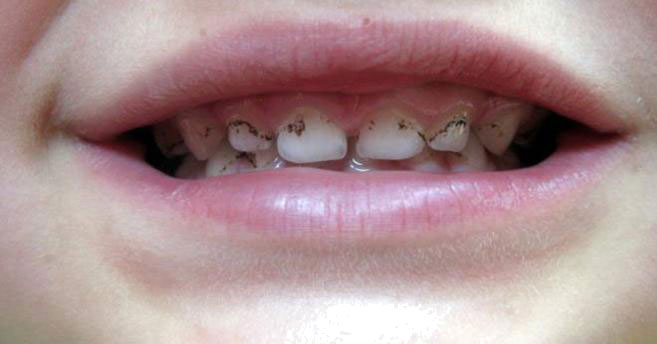
Milk tooth staining
Black colors are often found in the case of baby teeth. Parents notice these stains and address the pedodontist worriedly.
These stains are located at the base of the tooth near the gum, at first, and if not intervened they can cover almost the entire surface of the tooth. It affects both baby and permanent teeth. They appear in childhood and can last until puberty, being rare in adults.
The cause of these stains are anaerobic chromogenic bacteria of the species Actynomices, and black spots are deposits of ferrous sulfates resulting from the chemical interaction of hydrogen sulfide produced by these anaerobic bacteria in saliva and iron in saliva.
Fortunately, these colors do not endanger the vitality of the teeth, but they are very unsightly, and can affect the child’s self-esteem.
The treatment is performed in the dental office and consists of complete sanitation (descaling, airflow, professional brushing) accompanied by a rigorous sanitation at home (morning and evening). Unfortunately, these spots reappear and it is recommended to repeat the professional hygiene every 4-6 months.
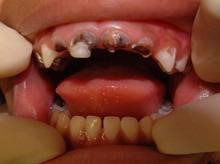
Baby bottle caries
Caria de biberon reprezinta o forma agresiva de carie care apare pe dintii de lapte ai copiilor sub 3 ani. Are o evolutie foarte rapida debutand sub forma unei pete alb-galbui, mergand pana la afectarea dintelui in intregime ajungand la stadiul de resturi radiculare.
Evolutia tipica a cariei de biberon urmeaza in general niste pasi specifici. Debuteaza prin afectarea dintilor frontali superiori (fara afectarea celor inferiori). Netratate cariile de biberon pot afecta intraga dentitie a copilului. Ordinea de aparitie a cariilor respecta in general ordinea de eruptie a dintilor de lapte.
The causes of bottle caries are many, but the main factor is the use of the bottle outside of meals. Carbohydrates in sweet liquids (sweetened tea, fruit juice, powdered milk, even breast milk) are a source of food for bacteria in the baby’s oral cavity. These bacteria produce acids that attack the teeth.
To prevent bottle caries, it is recommended:
- grooming the baby’s gums after each meal with a piece of gauze (even if the first teeth have not yet erupted);
- the beginning of the tooth brushing with the appearance of the first teeth;
- do not let the baby fall asleep with the bottle of milk juice or tea in the mouth;
- avoiding sweet foods as much as possible;
The treatment of bottle caries is of two types:
Preventive (by educating parents about healthy eating habits)
curative , performed by the pedodontist depending on the clinical situation (fluoridation, fillings, endodontic treatment, extractions)
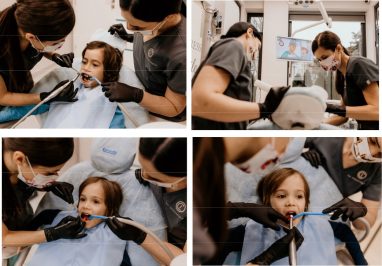
Treatments of dental diseases in children
Treatments for children performed in the dental office include prophylaxis treatments (prevention) of dental diseases and curative treatments.
Prophylactic treatments
- sanitation (professional brushing, airflow, descaling);
- sealing baby teeth / young teeth;
- topical fluoridation;
Sealing teeth
Sealing is a measure to prevent the appearance of caries on the dental surfaces that present
ditches and dimples, ie at the level of molars and premolars (sanitization of these ditches by children, being more difficult to achieve). The main teeth that benefit from this measure are 6-year-old molars, premolars and 12-year-old molars as they erupt. In some cases, the pedodontist may also recommend sealing temporary molars (increased risk of caries due to unsatisfactory hygiene and high consumption of sweets), for safer prevention.
Dental sealing is done with a resinous liquid that is applied to the surface of the tooth and fills the grooves and dimples of the tooth. This prevents the deposition of food and bacteria in these retentive spaces and difficult to access the toothbrush.
The procedure is a short one that does not require anesthesia or tooth preparation with a milling cutter. The tooth should be cleaned after which a gel is applied which is left to act for about a minute. The tooth is then washed and dried after which the sealing material is applied (it can be white, tooth-colored or colored). The material hardens with ultraviolet light.
The sealing material stays on the tooth surface for about two years, ensuring its protection against caries. Periodic inspections and restoration of seals as needed are recommended.
Seals do not provide complete protection against tooth decay. A complete prevention involves:
- complete brushing (at least twice a day);
- flossing;
- Topical fluoridation;
- periodic checks (once every 4-6 months);
- orthodontic treatments;
Topical fluoridation
Topical dental fluoridation is a measure to prevent tooth decay by strengthening tooth enamel, making it more resistant to tooth decay.
Professional fluoridation is performed in the dentist’s office by the pedodontist. After sanitization, fluoride is applied with a brush. Fluoride can be in the form of paste, gel or varnish. It is kept for a few minutes to allow it to penetrate the enamel structure. This procedure must be performed in the dental office for a better quality, lasting effect, but also because there are certain risks, the excess fluoride being toxic to the body.
Curative Treatments :
- treatment of emergencies (fractures, dislocations, dental avulsions)
- treatment of tooth decay of baby teeth and permanent teeth
- Extractions of baby teeth
Parafunctions and vicious habits of children
The pedodontist must pay special attention to the discovery of any vicious habits or dental parafunctions.
Among the vicious habits, we mention:
- finger suggestion;
- biting the lower or upper lip;
- interposing different objects between arcades;
Among parafunctions, we mention:
- oral respiration;
- infant swallowing (during swallowing, the child interposes his tongue between the arches);
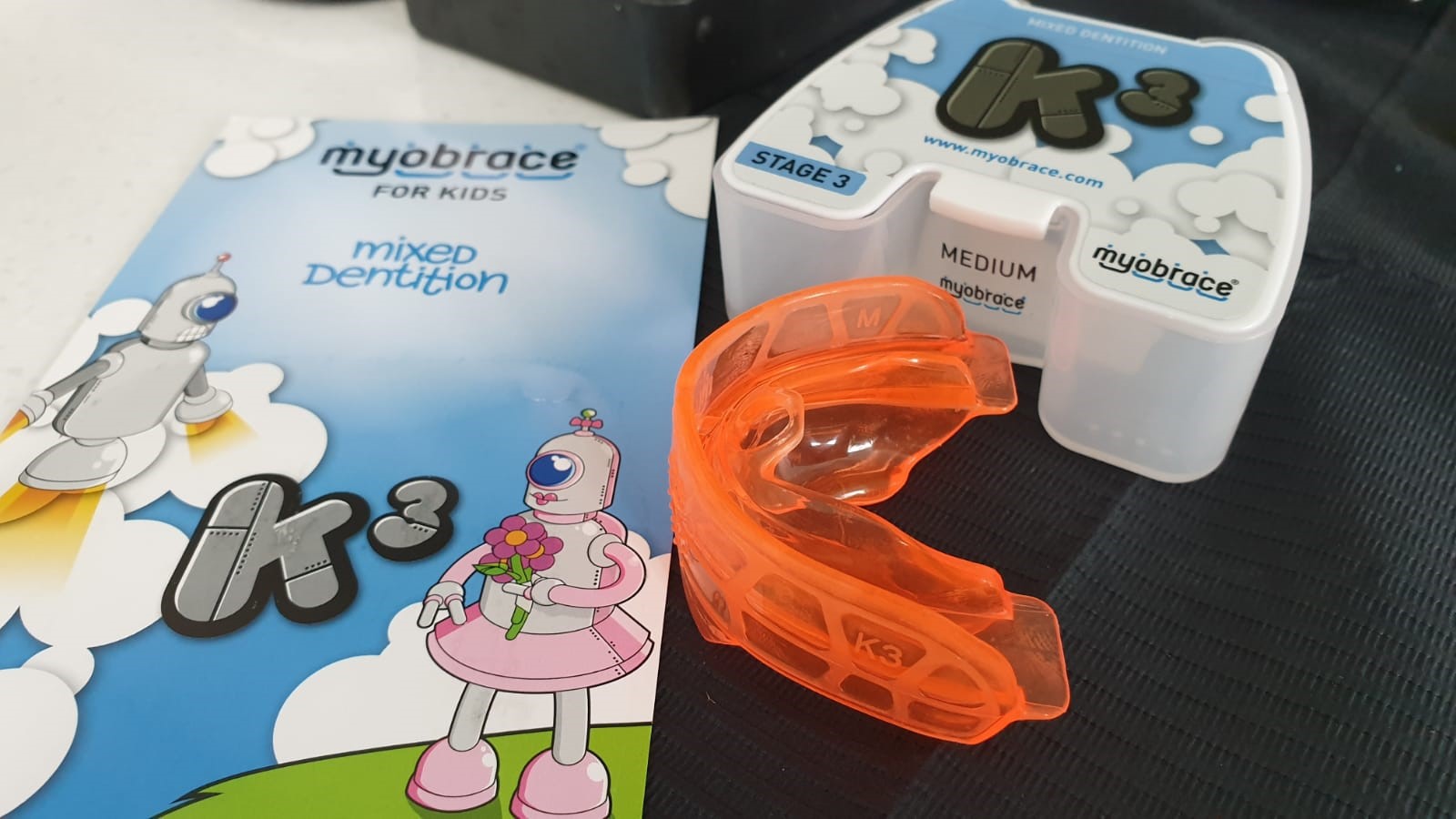
Correcting parafunctions and removing vicious habits are very important for the proper development of dental arches and jaw bones. In case of observing them, the pedodontist will recommend different exercises and wearing certain braces. In our clinic we use the so-called “ trainers “.
Trainers are the more modern version of the classic mobilizable devices (with wires and acrylate), being made of a softer or less soft silicone, depending on the treatment stage, being more comfortable for children and having a shorter wearing time (2h evening + night), compared to the classic ones (8h day + night).
Trainer treatments help us to:
- correcting vicious habits;
- development and alignment of the maxillary bones;
- straightening teeth;
- improving facial development;
- improving general health;
How do you accomplish these things? Helping the child to:
- breathe through the nose (not the mouth);
- to correct the resting position of the tongue (to an anterior position and not fallen to the posterior);
- to swallow correctly (with the tip of the tongue on the roof of the mouth);
- keep his lips in contact when swallowing;
The trainers are chosen according to the dental anomaly, the size of the child’s arch and according to the treatment stage. They have different sizes and colors, which makes them more attractive, and the treatment is usually carried out in 3 stages:
- Correction of vicious habits and parafunctions – stage 1;
- Development of arches and dental alignment – stage 2;
- Final alignment and content contention – stage 3;




